Home > Wednesday Wisdoms: Newsletter >From Okay to Outstanding: Upgrade Your Econ Essays with Rich Vocabulary!
Jump to Section:
From Okay to Outstanding: Upgrade Your Econ Essays with Rich Vocabulary!
Will curbs to migration hit the UK economy?
Summary
A Level Economics Questions:
Possible A Level Economics 25 Marker Question
Infographic of the Week
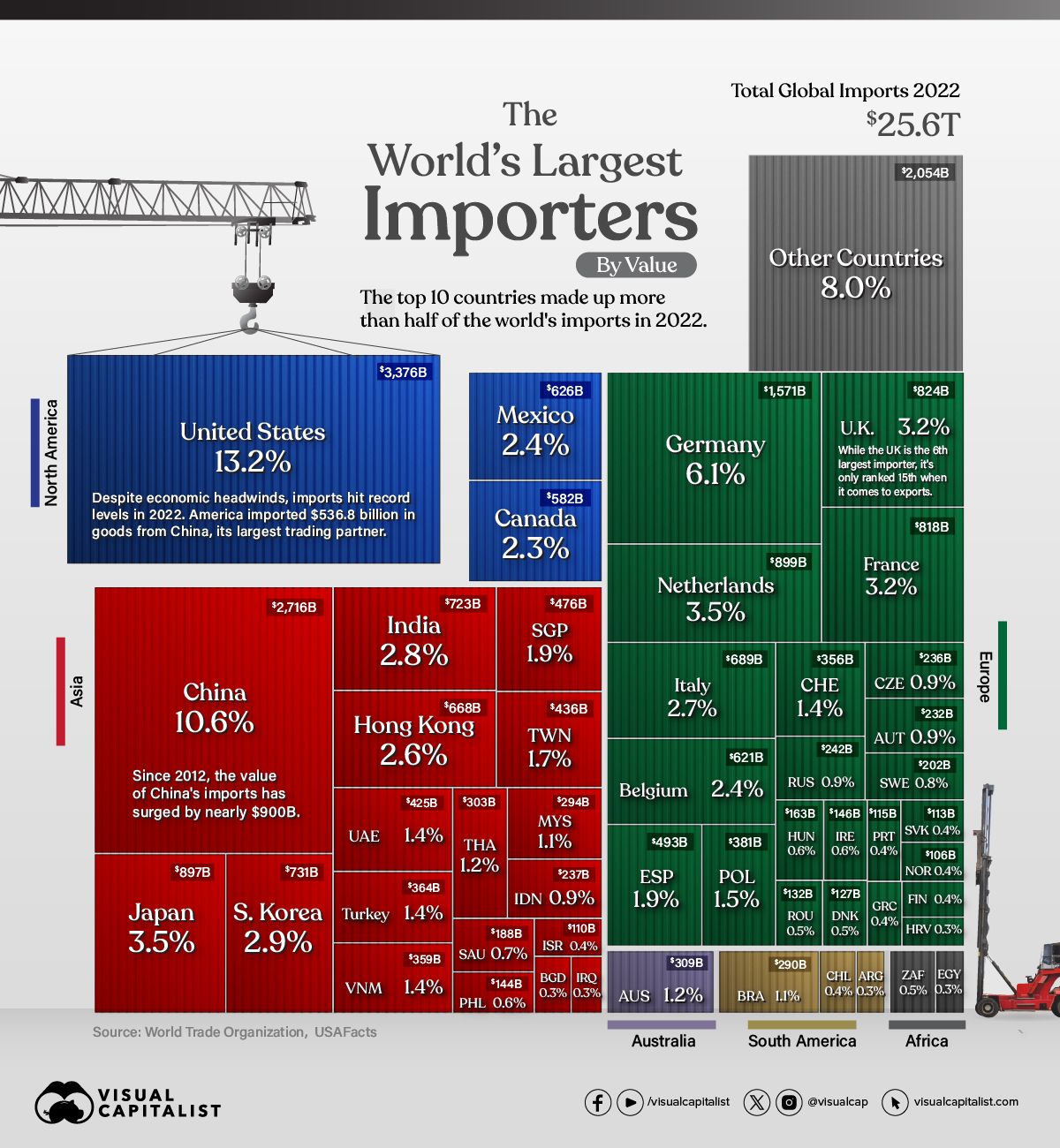
Global Import Dynamics: Key Players and Emerging Trends in 2022
In 2022, global imports soared to a staggering $25.6 trillion, mirroring the U.S. GDP in scale. The U.S. topped the chart as the largest importer with $3.4 trillion, despite a backdrop of inflation and market uncertainty, marking a 15% annual increase. China followed with $2.7 trillion in imports, albeit with a modest 1% growth. European nations like Germany ($1.57 trillion) and the Netherlands ($899 billion) featured prominently, with the EU leading in agricultural, fuel, mining, and automotive product imports. Global import volumes are projected to contract by up to 1.2% in 2023 across key regions, partly due to reduced manufacturing demand. Intermediate goods, crucial in production chains, saw a decrease in trade share to 48.5% from a three-year average of 51%. Factors such as subsidies, export bans, and local production incentives like the U.S.'s $52.7 billion CHIPS Act are influencing these trade patterns, hinting at possible trends towards de-globalisation.
Chart of the Week
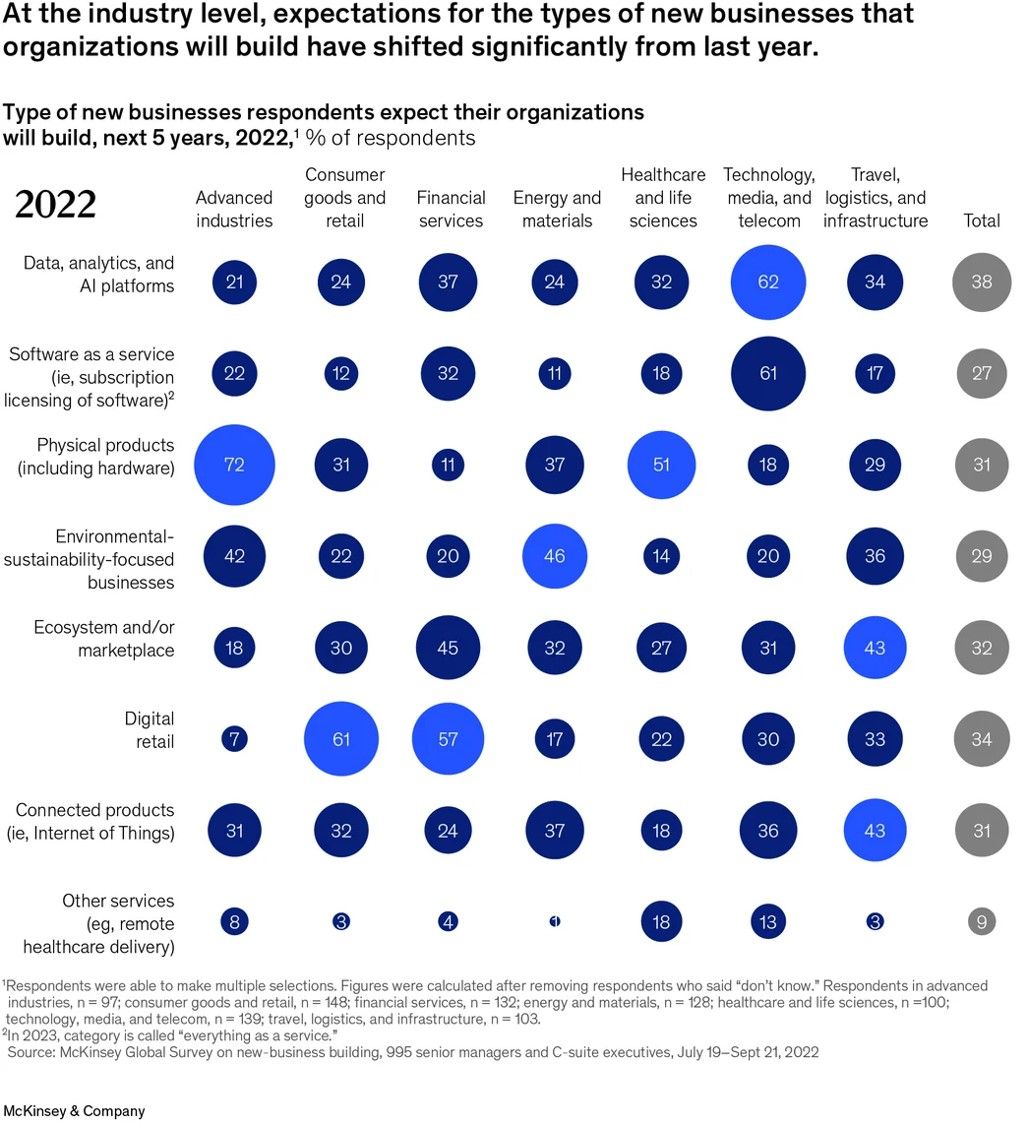
Emerging Business Trends: Navigating Shifting Expectations in Industry Sectors
The graph presents a compelling overview of the changing landscape for new business creation across various industries. In 2022, respondents anticipate the most significant growth in 'Physical products' for advanced industries, with a notable 72% expecting their organisations to build in this sector. Meanwhile, the 'Technology, media, and telecom' sector is projected to focus primarily on 'Data, analytics, and AI platforms', with 62% of respondents seeing this as a key area of expansion. A substantial shift towards 'Environmental sustainability-focused businesses' is also evident, especially in the energy and materials industry, with 46% of respondents foreseeing growth. The healthcare and life sciences sector shows a strong inclination towards 'Connected products', such as the Internet of Things (IoT), with 51% of respondents predicting an emphasis here. The data reflects a strategic pivot towards technologically advanced and sustainability-focused business models, signaling an adaptation to global economic and environmental challenges.
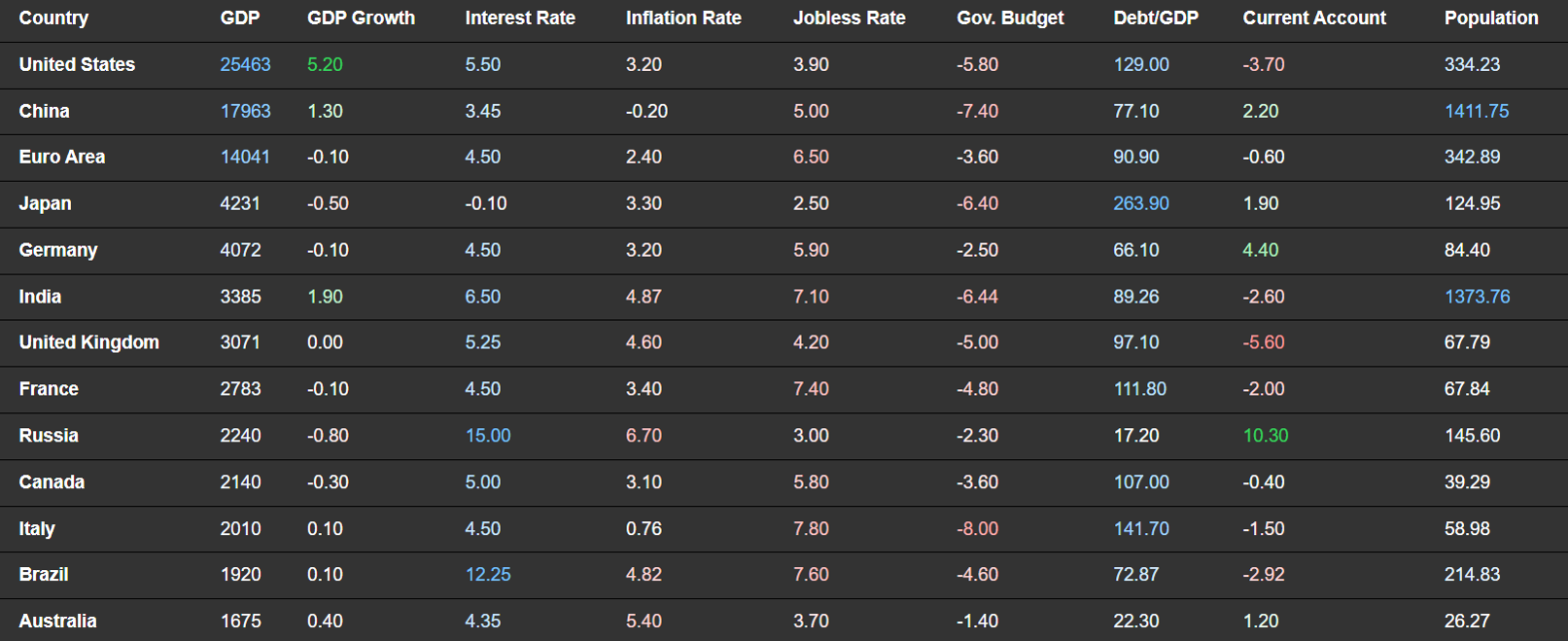
Macroeconomic Data
Whenever you're ready there is one way I can help you.
Emre Aksahin
Chief Learning Officer at Edgenie


