Home > Edgenie Sunday Schroll: Newsletter > How Can I Boost My A-Level Economics Grades? 📈
Jump to Section:
Not Seeing Results? Here's How to Level Up Your Economics Revision
Why orange juice has never been more expensive
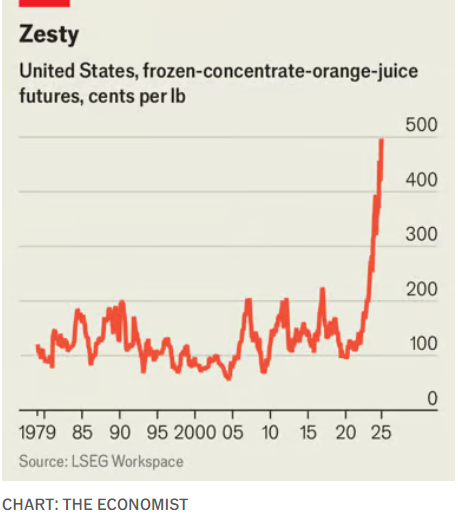
Summary
A Level Economics Questions:
Possible A Level Economics 25 Marker Question
Infographic of the Week
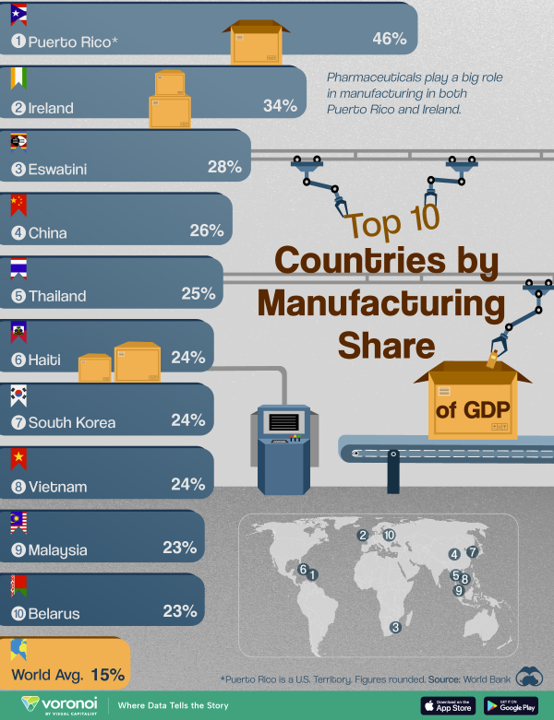
Top 10 Economies with the Highest Manufacturing Contribution to GDP
While services dominate most of the world’s largest economies, manufacturing remains vital in certain countries. Puerto Rico and Ireland lead the top 10 economies where manufacturing significantly contributes to GDP, driven by their strong pharmaceutical industries. Puerto Rico, once a hub for American pharmaceutical exports, and Ireland, a key vaccine producer, each rely on manufacturing for over 30% of their GDP. Asia also plays a central role, with five countries—China, South Korea, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Thailand—forming important manufacturing hubs, particularly for electronics and broadcasting equipment. Globally, manufacturing averages 15% of GDP.
Chart of the Week
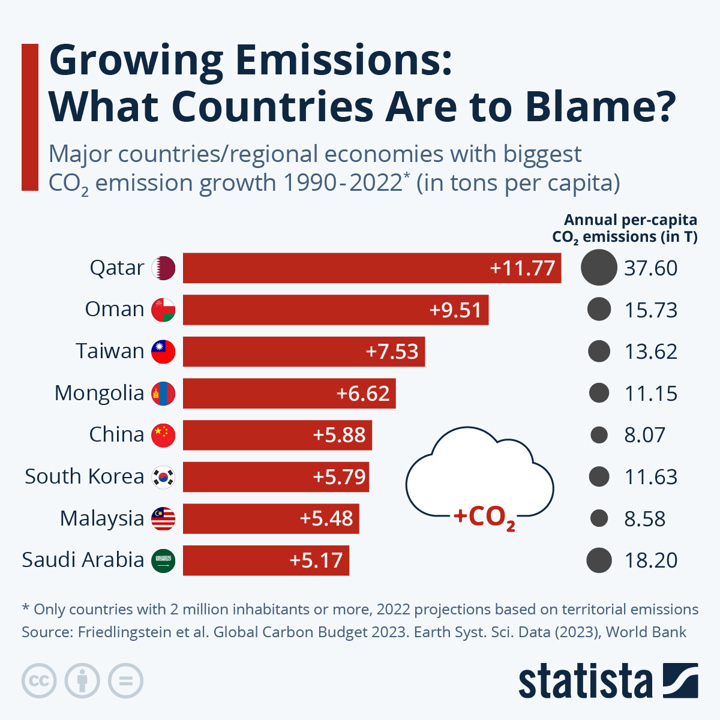
Growing CO₂ Emissions: Major Contributors
Between 1990 and 2022, several countries, particularly on the Arabian Peninsula and in Asia, saw the highest growth in per-capita CO₂ emissions. Qatar leads with an increase of 11.77 tons per capita, followed by Oman, while Saudi Arabia also ranks high due to the availability of cheap oil and gas. Asian nations like Taiwan and South Korea show significant growth due to their strong manufacturing sectors and reliance on waste-to-energy practices. China and Malaysia, though showing high per-capita CO₂ emission growth, have lower annual emissions compared to other top emitters on the list.
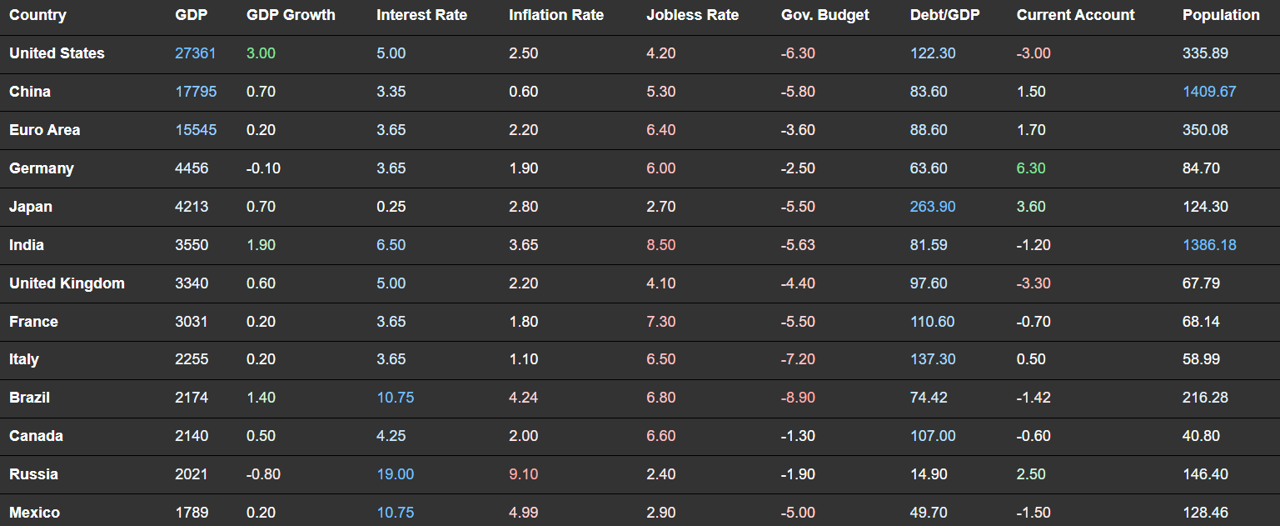
Macroeconomic Data
Whenever you're ready there is one way I can help you.
Emre Aksahin
Chief Learning Officer at Edgenie


