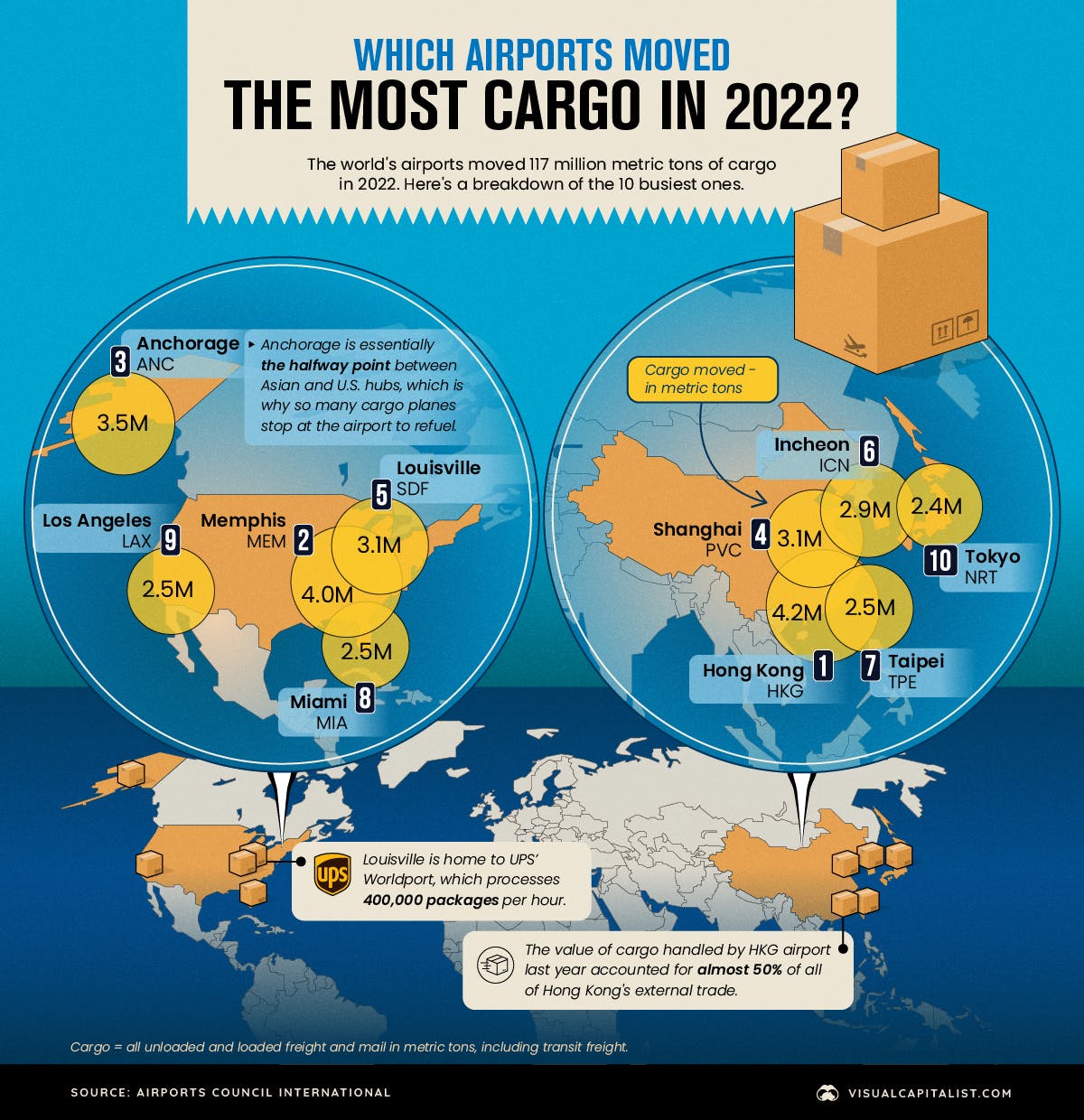
BMW's Oxford Plant:BMW plans to invest up to £600m for future electric Mini production.
The UK government offers £75m in support.
Production Shifts:
Electric Minis started in Cowley in 2019.
BMW moved most electric car production to China and some to Leipzig, Germany.
Oxford remains the "home of the Mini". All Minis to be electric by 2030.
UK Car Industry Changes:
2022 car production hit the lowest since 1956.
Honda's Swindon and Ford's Bridgend plants closed recently.
Britishvolt's "gigafactory" plans collapsed but were taken over by Recharge Industries.
Other Investments:
Ford invests £380m for electric vehicle motors in Halewood.
Stellantis backs electric van production in Ellesmere Port with £100m.
Government-funded gigafactory construction ongoing next to Nissan's Sunderland plant.
Government Aims:
UK government aims for a stake in the electric car market.
Jaguar Land Rover's parent company, Tata, in talks for potential UK gigafactory funding.
Spain is also competing for this investment
Q:
Using the case of BMW's £600m investment and the UK government's offer of £75m in support, discuss the potential economic benefits and drawbacks of government intervention in the automobile industry. How might this support influence BMW's long-term production decisions?
A:Benefits of Government Intervention
Stimulates Production: The £75m support could act as a catalyst for further investments, encouraging production to remain or increase in the UK.
Job Security: Can prevent potential layoffs or provide job opportunities, given that companies might be more inclined to operate in the region due to the financial incentives.
Technological Advancements: Subsidised investments can lead to research and development, pushing the industry's technological boundaries.
Drawbacks:
Misallocation of Resources: The government might invest taxpayer money into projects that don't necessarily yield a long-term economic return.
Moral Hazard: Firms might become reliant on government bailouts or support, leading them to take unwarranted risks.
Influence on BMW: The support could make BMW maintain its operations in the UK, anticipating more subsidies and leading to long-term commitments to the region.
Q: Analyse the economic factors that might have influenced BMW's decision to move most of its electric car production to China and some to Leipzig, Germany. Using the data of the UK car production in 2022 being the lowest since 1956, comment on the potential reasons and implications for such a decline in domestic production.
A:
Factors for BMW's Production Shift:
Cost Efficiency: Producing in China could be cheaper due to lower labour and manufacturing costs.
Market Proximity: Being closer to the large Asian market allows for quicker distribution and responsiveness to market changes.
Joint Ventures: Collaborations, like with Great Wall Motor, can offer technological and market advantages.
Decline Reasons and Implications:
Potential Causes: Brexit uncertainties and global competition.
Implications: Economic slowdown, job losses, and a potential decline in foreign direct investment.
Q: Evaluate the potential economic impact on the UK's economy of significant plant closures, such as Honda's Swindon and Ford's Bridgend. How might these closures, combined with Britishvolt's initial collapse, affect employment, foreign direct investment, and economic growth in the short and long term?
A: Economic Impacts:
Direct Unemployment: Immediate job losses from the closure of plants.
Indirect Effects: Suppliers and dependent sectors might face losses, leading to further unemployment.
Reduced FDI: Closures might signal instability or unprofitability, deterring future foreign direct investments.
GDP Reduction: The automobile sector, a significant contributor to the UK's GDP, will see reduced outputs. Britishvolt's collapse signals potential volatility in the electric battery sector, crucial for the transition to electric vehicles.
Q: Discuss the potential economic outcomes of government-backed projects, such as Ford's £380m investment in Halewood and the £100m backing for Stellantis in Ellesmere Port. How might public funding change the competitive dynamics of the electric car market in the UK?
A: Economic Outcomes:
Stimulated Production: The likes of Ford's and Stellantis's investments, with government backing, can increase electric vehicle production in the UK.
Technological Progress: Such funding can lead to research, innovation, and the development of more efficient electric vehicles.
Increased Competition: Financial backing can level the playing field, allowing UK manufacturers to compete more effectively with international players. This, in turn, positions the UK as a key player in the global electric vehicle industry.