Home > Wednesday Wisdoms: Newsletter > This is how you score A* Evaluation marks 🎯
Jump to Section:
Mastering the art of evaluation is crucial. 🎯
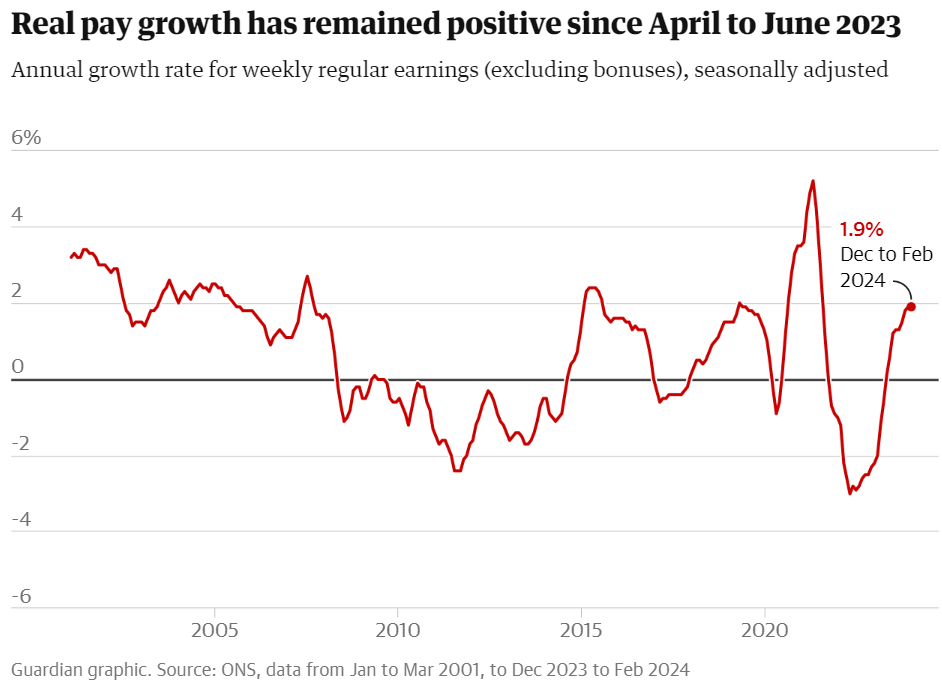
UK unemployment rate leaps to 4.2% amid fears of job cuts
Summary
A Level Economics Questions:
Possible A Level Economics 25 Marker Question
Infographic of the Week
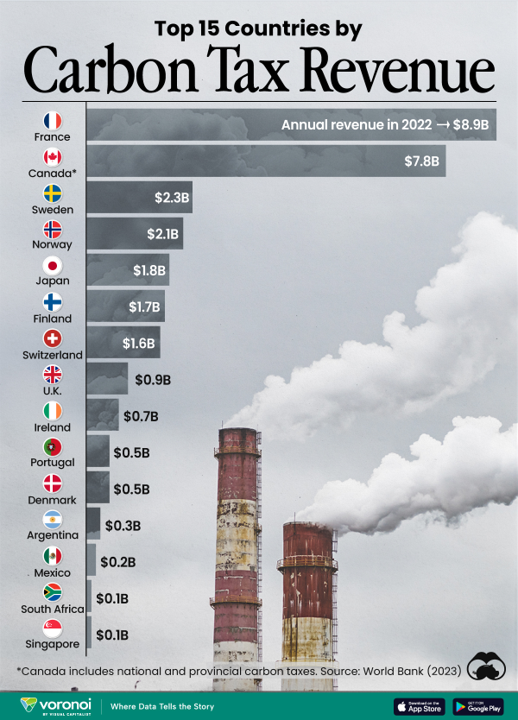

France and Canada Dominate Global Carbon Tax Revenue in 2022
In 2022, France and Canada emerged as leaders in generating carbon tax revenue, collectively accounting for over half of the global total of approximately $30 billion. This financial outcome underscores the effectiveness of their extensive carbon pricing frameworks that span multiple sectors, such as transportation and industry. The top 15 countries in carbon tax revenue, according to the World Bank’s State and Trends of Carbon Pricing Report from April 2023, also include Sweden, Norway, and Japan among others. Despite the significant revenue generated, there is a consensus that carbon pricing alone may not suffice to meet the ambitious targets of the Paris Climate Agreement. This highlights the need for additional policy measures and technological innovations to complement the carbon taxes and drive more substantial reductions in CO2 emissions.
Chart of the Week
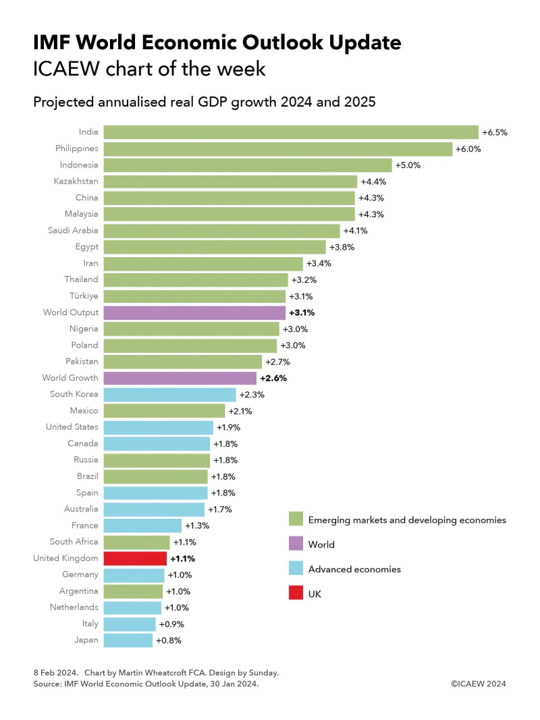
Global Economic Growth Forecasts: A Tale of Two Extremes
The International Monetary Fund's latest World Economic Outlook, released every January, predicts a global economic growth rate of 2.6% for 2024 and 2025 based on market exchange rates, and 3.1% when adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP). The report highlights a disparity between emerging markets and developed economies, with the former generally outpacing the latter. Notably, India leads the growth among emerging markets, while advanced economies like the EU show modest improvement. The US and China, although still significant contributors to the global economy, are expected to see a slowdown compared to 2023. On the other hand, countries like Argentina face economic contraction in 2024 but are anticipated to recover strongly in 2025. The report underlines varied growth trajectories, indicating a complex global economic landscape recovering from the pandemic.
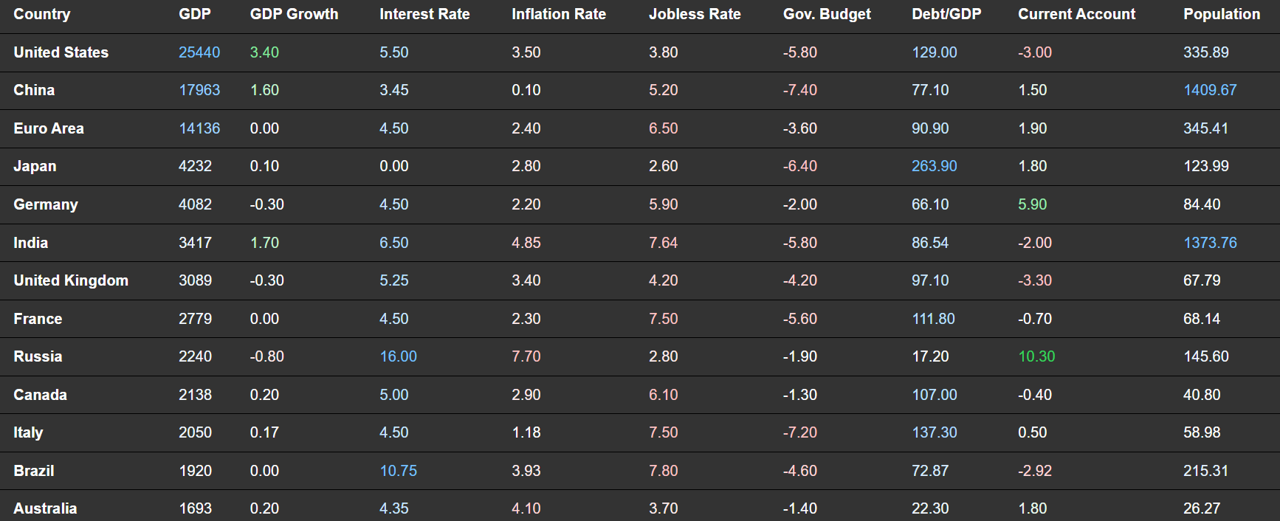
Macroeconomic Data
Whenever you're ready there is one way I can help you.
Emre Aksahin
Chief Learning Officer at Edgenie


