Home > Wednesday Wisdoms: Newsletter > What If You Can't Think of Points on a Question in an Exam?
Jump to Section:
What If You Can't Think of Points on a Question in an Exam?
Productivity soars in sectors of global economy most exposed to AI, says report
Summary
A Level Economics Questions:
Possible A Level Economics 25 Marker Question
Infographic of the Week
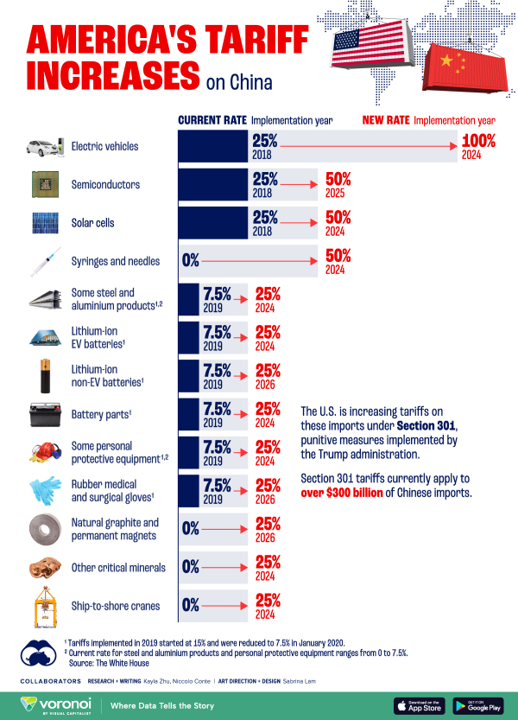
U.S. Imposes New Tariffs on Chinese Goods, Targeting EV and Medical Industries
The U.S. has announced a significant increase in tariffs on over $18 billion worth of Chinese imports, with new rates targeting the electric vehicle (EV) and medical sectors. This move, aimed at countering China's "unfair trade practices," includes raising tariffs on EVs from 25% to 100% and introducing new tariffs on critical minerals essential for battery production. Medical products like surgical gloves and personal protective equipment, previously exempt due to COVID-19, now face new tariffs, including a 50% rate on syringes and needles. These tariffs, enacted under Section 301, continue the trade policies initiated in 2018, affecting a broad range of goods and escalating the long-standing trade tensions between the U.S. and China.
Chart of the Week
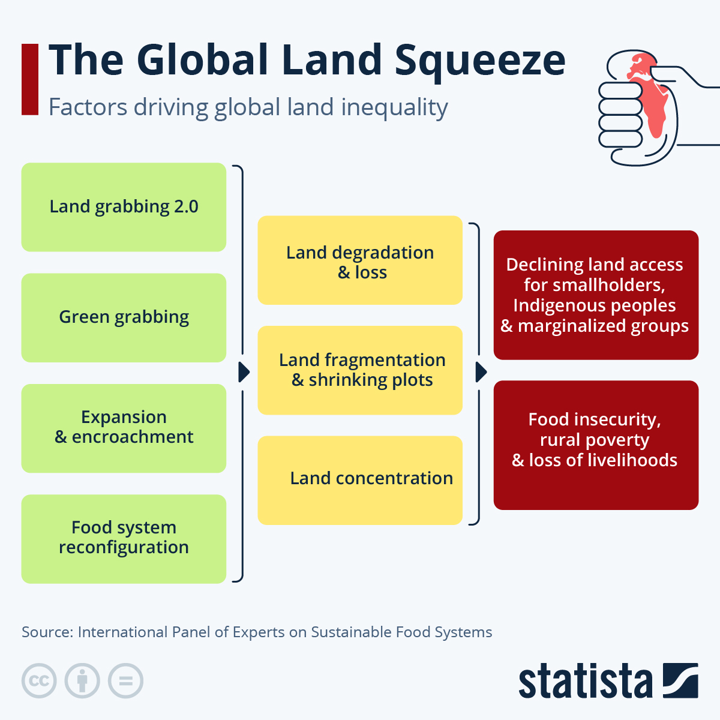
The Global Land Squeeze and Its Impact on Smallholder Farmers
Smallholder farmers worldwide are facing a phenomenon known as "land squeeze," which is deepening rural poverty and land inequality. This issue is driven by the consolidation of large farms, leading to fragmented and smaller plots for smallholders. In Asia, land inequality has risen by 11% since 1980, and globally, 1% of the largest farms control 70% of farmland. According to the International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems' report, "Land Squeeze," factors such as land grabbing, green grabbing for carbon offset projects, industrial encroachment, and urbanisation contribute to this issue. These pressures diminish the access and control over land for farmers, Indigenous Peoples, and marginalized groups, threatening their livelihoods and food security. The report highlights that these processes are rooted in a history of dispossession and discrimination against smallholders and traditional communities.
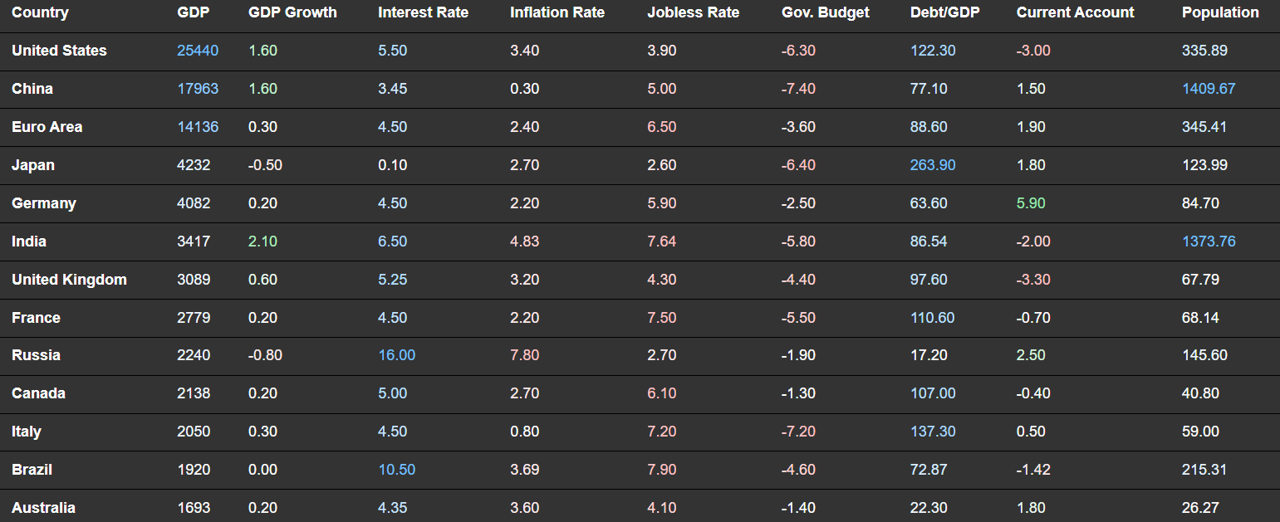
Macroeconomic Data
Whenever you're ready there is one way I can help you.
Emre Aksahin
Chief Learning Officer at Edgenie


